Creating and Migrating Datasets¶
Overview¶
A dataset on the EDP represents a collection of records indexed with a specific schema (i.e. a list of fields). Datasets make it easy to query and filter datasets of any size in real-time.
Datasets can be created with a predefined schema (using a Dataset template) or without any fields. The platform will always detect new fields in imported records and assign data types; however, users are recommended to use templates so that the data types of fields can be set in advance. Records can be added to datasets in multiple ways such as transforming files into datasets, programmatically generating records, or copying records from other datasets using “dataset migrations”.
Datasets are designed to be a flexible and scalable solution for storing structured JSON-compatible data. The molecular data landscape is filled with a large variety of unique file formats, each with its own subtleties and quirks. On the EDP, almost any data source can be imported into a dataset as long as it can be transformed into JSON. The EDP supports many formats, making it easy to import data into a dataset. Once the data has been imported into a dataset, users can take advantage of the many features they offer: scalability, portability, version control, flexibility of schemas, querying and filtering of data as well as annotation and analysis using Expressions.
Creating Datasets¶
To start working with datasets on the EDP, users can create new, empty datasets “from scratch”. Datasets have both a schema (dataset fields) and contents (dataset records). On the EDP, users don’t need to know their schema in advance (fields are automatically detected from imported data). However, in many cases crafting a schema (i.e. setting dataset fields) can help avoid issues with data types and field names.
To create a dataset, users can supply a full path in the following format:
<domain>:<vault>:<path>
For example, for a new dataset within a folder in a shared vault:
myDomain:MyVault:/folder/dataset
Or for a new dataset within a folder in a user’s personal vault (represented by “~/”):
~/folder/dataset
In Python:
from quartzbio import Dataset
# Create a new, empty dataset in your personal vault (represented by "~/")
dataset = Dataset.get_or_create_by_full_path('~/my_dataset')
When creating the dataset, users can supply a number of optional parameters:
description: A description (text) of the dataset.
fields: A list of field objects.
capacity: A performance optimization for datasets that will have tens or hundreds of millions of records. The default is “small” but can be set to “medium” or “large”. This cannot be changed once it has been set.
metadata: A dictionary of key/value pairs that can be associated with the dataset.
tags: A list of strings (tags) that can be associated with the dataset.
Once the dataset is created it will be empty (containing no records) and consist of the default EDP _id field and any other fields that may have been added to the fields parameter. Fields beginning with an underscore such as _id and _commit are considered reserved and may be modified during an import. The _id field represents the unique ID for each record, which can be used to edit or delete individual records. The value of _id cannot be edited once a record is saved. The _commit field is always reset during the commit process and makes it possible to track and log all changes made to a Dataset.
Dataset Fields¶
By default, new fields are automatically detected by the import system when transforming a file into a dataset. Users can also provide a list of fields (i.e. a template) using the fields parameter and explicitly set names and titles, data types, ordering, descriptions, and entity types for each field.
Dataset fields have the following properties:
Property |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
name (required) |
string |
The “low-level” field name, is used in JSON-formatted records. |
data_type |
string |
A valid data type. |
description |
string |
Free text that describes the contents of the field. |
entity_type |
string |
A valid EDP entity type. |
expression |
string |
A valid EDP expression. |
is_hidden |
boolean |
Set to True if the field should be excluded by default from the UI. The default is False. |
is_list |
boolean |
Set to True if multiple values are stored as a list. The default is False. |
ordering |
integer |
The order in which this column appears in the UI and in tabular exports. |
title |
string |
The field’s display name is shown in the UI and in tabular exports. Default is set automatically from the name. |
is_transient |
boolean |
Set to True if the field is a temporary field used for the purposes of easier data & expression manipulation during imports & migrations. The default is False. |
depends_on |
list of strings |
List of fields that must have expressions run first before this field’s expression is evaluated. In other words, what other fields that this field depends on? The default is an empty list. |
url_template |
string |
A URL template with one or more “{value}” sections that will be interpolated with the field value and displayed as a link in the dataset table |
Users should note that double underscores (“__”) should not be used in dataset field names.
The following example creates a new dataset using a template with two fields:
In Python:
from quartzbio import Dataset
from quartzbio import DatasetField
fields = [
{
"name": "my_string_field",
"description": "Just a string",
"data_type": "string",
"is_list": False,
"is_hidden": False,
"ordering": 0
},
{
"name": "gene_symbol",
"description": "HUGO gene symbol",
"data_type": "string",
"entity_type": "gene"
}
]
dataset_full_path = '~/python_examples/my_fields_dataset'
## Fields, capacity, and other optional parameters can be set during dataset creation
dataset = Dataset.get_or_create_by_full_path(
dataset_full_path,
fields=fields,
capacity='small'
)
## If the dataset already exists, you can add additional fields:
DatasetField.create(
dataset_id=dataset.id,
name="my_new_field",
data_type="string")
## Fields can also be edited
field = dataset.fields("my_string_field")
field.description = "A new description"
field.save()
URL Template
If users add a url_template value to the dataset field, the dataset table will show the value as a link in the EDP UI. This is useful for linking to other sources/websites. The dataset below has links for the gene and variant pages on EDP:
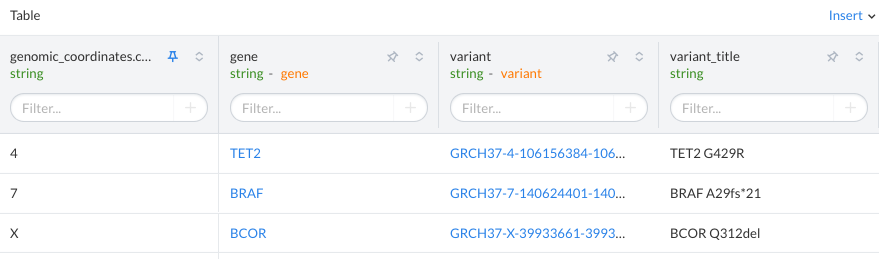
URL Template: Adding a value to the url_template property of a field will link it to the field values in the EDP web interface.
Migrating Datasets¶
Users can perform dataset “migrations” to copy data between or within datasets as well as use Python-based EDP Expressions to transform data during migrations. As such, migrations allow users to modify datasets in-place, making it possible to add, edit, and remove fields. All dataset migrations have a source dataset and a target dataset (which can be the same when editing a single dataset).
Copying Datasets¶
Copying a dataset is the simplest dataset migration. In this case, a new dataset is created (the target) and all the records from a source dataset are copied to it. The source dataset remains unchanged. Copying datasets can be useful if users do not want to alter the source dataset or if they do not have write access to the source dataset.
If users do not want to copy the entire source dataset, they can provide filter parameters to copy a subset. This example copies all BRCA1 variants from ClinVar into a new dataset:
In Python:
from quartzbio import Dataset
## Retrieve the source dataset
source = Dataset.get_by_full_path('quartzbio:Public:/ClinVar/5.2.0-20210110/Variants-GRCH37')
## Create your new target dataset
target = Dataset.get_or_create_by_full_path('~/python_examples/clinvar')
## Copy all variants in BRCA1
query = source.query().filter(gene='BRCA1')
query.migrate(target=target)
Modifying Fields¶
The title, description, url_template, ordering, and entity_type of a field can be modified at any time. Field names cannot be renamed and fields cannot be removed in-place, though they can be hidden by setting the is_hidden parameter to TRUE. To change the name of a field, users must perform a dataset migration to create a new field with the desired name in the cloned dataset. Similarly, to remove a field from a dataset, it must be cloned to a new dataset that does not have the field the user intends to delete. For more information about modifying datasets, users can refer to the Modifying Datasets documentation.
The following example renames the field of the dataset through a dataset migration:
In Python:
import quartzbio as sb
dataset = sb.Dataset.get_or_create_by_full_path("dataset_id")
## We want to transform the data by passing target_fields.
## Because there is no "rename" functionality, the workaround is to create new fields from with the values from the old fields. Set is_transient=TRUE for the old fields so that they are just temporarily used during data transform, and not included in the output.
## The new fields just take the value of the old fields.
target_fields = [
{
"name": "old_field_name",
"is_transient": True
},
{
"name": "new_field_name",
"data_type": 'string',
"expression": "record.old_field_name"
}
]
## Create migration
migration = dataset.migrate(target=dataset, target_fields=target_fields)
API Endpoints¶
Methods do not accept URL parameters or request bodies unless specified. Please note that if your EDP endpoint is sponsor.edp.aws.quartz.bio, you would use sponsor.api.edp.aws.quartz.bio.
Datasets
Method |
HTTP Request |
Description |
Authorization |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
create |
POST https://<EDP_API_HOST>/v2/datasets |
Create a dataset. |
This request requires an authorized user with permission to create new datasets. |
The response contains a single Dataset resource. |
Request Body:
Property |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
name |
string |
The unique name within the vault for this dataset. |
vault_id |
integer |
The vault version in which to create the dataset. |
vault_parent_object_id |
integer |
The folder ID in which to create the dataset. Use ‘null’ to place at ‘/’. |
fields |
Dataset Fields |
A list of dataset field objects. |
metadata |
object |
A dictionary of key/value pairs. |
tags |
string |
A list of strings to organize the dataset. |
capacity |
string |
(Optional) The dataset capacity level (small, medium, or large). |
storage_class |
string |
(Optional) The dataset storage class. |
Method |
HTTP Request |
Description |
Authorization |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
delete |
DELETE https://<EDP_API_HOST>/v2/datasets/{DATASET_ID} |
Delete a dataset. |
This request requires an authorized user with permission to modify the target dataset. |
The response returns “HTTP 200 OK” when successful. |
Method |
HTTP Request |
Description |
Authorization |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
get |
GET https://<EDP_API_HOST>/v2/datasets/{DATASET_ID} |
Retrieve metadata about a dataset. |
This request requires an authorized user with permission to view the target dataset. |
The response contains a Dataset resource. |
Dataset Fields
Method |
HTTP Request |
Description |
Authorization |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
create |
POST https://<EDP_API_HOST>/v2/dataset_fields |
Create a dataset field. |
This request requires an authorized user with write permission on the dataset. |
The response contains a single DatasetField resource. |
Request Body:
In the request body, provide an object with the following properties:
Property |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
data_type |
string |
A valid data type (see below). |
description |
string |
Describes the contents of the field. |
entity_type |
string |
A valid entity type. |
expression |
string |
A valid expression. |
is_hidden |
boolean |
Set to True if the field should be excluded by default from the UI. |
is_list |
boolean |
Set to True if multiple values are stored as a list. |
name |
string |
The “low-level” field name, used in JSON formatted records. Field names are immutable once set. The title and description of a field can always be changed. |
ordering |
integer |
The order in which this column appears when retrieving data from the dataset. Order is 0-based. Default is 0 |
title |
string |
The field’s display name, shown in the UI and in CSV/Excel exports. |
url_template |
string |
A URL template with one or more “{value}” sections that will be interpolated with the field value and displayed as a link in the dataset table. |
Data Types:
Data Type |
Description |
|---|---|
auto (default) |
Attempt to automatically detect the data type upon the first import. |
boolean |
Either True, False, or null. |
date |
A string in ISO 8601 format, for example: “2017-03-29T14:52:01”. |
double |
A double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 floating point. |
float |
single-precision 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point. |
integer |
A signed 32-bit integer with a minimum value of -2E+31 and a maximum value of (2E+31)-1. |
long |
A signed 64-bit integer with a minimum value of -2E+63 and a maximum value of (2E+63)-1. |
object |
A key/value, JSON-like object, similar to a Python dictionary. |
string |
A valid UTF-8 string up to 32,766 characters in length. |
text |
A valid UTF-8 string of any length, indexed for full-text search. |
blob |
A valid UTF-8 string of any length, not indexed for search. |
Method |
HTTP Request |
Description |
Authorization |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
get |
GET https://<EDP_API_HOST>/v2/dataset_fields/{ID} |
Retrieve a dataset field. |
This request requires an authorized user with read permission on the dataset. |
The response contains a DatasetField resource. |
Method |
HTTP Request |
Description |
Authorization |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
list |
GET https://<EDP_API_HOST>/v2/datasets/{DATASET_ID}/fields |
Retrieve a set of dataset fields for a dataset. |
This request requires an authorized user with read permission on the dataset. |
The response contains a list of DatasetField resources. |
Parameters:
Property |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
limit |
integer |
The number of objects to return per page. |
offset |
integer |
The offset within the list of available objects. |
Method |
HTTP Request |
Description |
Authorization |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
update |
PUT https://<EDP_API_HOST>/v2/dataset_fields/{ID} |
Update a dataset field. |
This request requires an authorized user with write permission on the dataset. |
The response contains the updated DatasetField resource. |
Request Body
In the request body, provide a valid DatasetField object (see create above).
Dataset Migrations
Method |
HTTP Request |
Description |
Authorization |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
create |
POST https://<EDP_API_HOST>/v2/dataset_migrations |
Create a dataset migration. |
This request requires an authorized user with read permissions from the source dataset, and write permissions to the target dataset. |
The response contains a new DatasetMigration resource. |
Request Body:
Property |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
commit_mode |
string |
A valid commit mode. |
include_errors |
boolean |
If True, a new field (_errors) will be added to each record containing expression evaluation errors (default: True). |
source_id |
integer |
The ID of a valid, queryable dataset. |
source_params |
object |
The query parameters used on the source dataset (see below). |
target_fields |
object |
A list of valid dataset fields to create or override in the target dataset. |
target_id |
integer |
A valid dataset with write permissions. |
entity_params |
object |
(optional) Configuration parameters for entity detection. |
validation_params |
object |
(optional) Configuration parameters for validation |
annotator_params |
object |
(optional) Configuration parameters for the Annotator. |
priority |
integer |
A priority to assign to this task. |
The following query parameters (source_params property) are supported for migrations:
Property |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
limit |
integer |
The number of records to migrate from the source dataset. |
filters |
objects |
A valid filter object. |
fields |
string |
A list of fields to include from the source dataset. |
exclude_fields |
string |
A list of fields to exclude from the source dataset. |
query |
string |
A valid query string. |
Method |
HTTP Request |
Description |
Authorization |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
delete |
DELETE https://<EDP_API_HOST>/v2/dataset_migrations/{ID} |
Delete a dataset migration. |
This request requires an authorized user with write permissions. |
The response returns “HTTP 200 OK” when successful. |
Method |
HTTP Request |
Description |
Authorization |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
get |
GET https://<EDP_API_HOST>/v2/dataset_migrations/{ID} |
Retrieve metadata about a dataset migration. |
This request requires an authorized user with permission. |
The response contains a DatasetMigration resource. |
Method |
HTTP Request |
Description |
Authorization |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
list |
GET https://<EDP_API_HOST>/v2/dataset/{DATASET_ID}/migrations |
Retrieve a list of dataset migrations for a dataset. |
This request requires an authorized user with read permission. |
The response contains a list of DatasetMigration resources from the specified source dataset. |
Parameters:
This request accepts the following parameters:
Property |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
limit |
integer |
The number of objects to return per page. |
offset |
integer |
The offset within the list of available objects. |
Method |
HTTP Request |
Description |
Authorization |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
cancel |
PUT https://<EDP_API_HOST>/v2/datasets_migrations/{ID}/cancel |
Cancel a dataset migration. |
This request requires an authorized user with read permission on the dataset. |
The response will contain a DatasetMigration resource with the status canceled. |
Request Body:
In the request body, provide a valid DatasetMigration object (see create above) with status = canceled.